Implement Roaming profile For Cross Border Trucks
What if your truck plies from Dubai to Oman? How could you set up roaming with a GPS tracking device? How can you possibly reduce/save on the roaming data charges?
In this post, I’m going to show you how to configure a Ruptela GPS device for a cross border truck in 5 easy steps.
Once configured, you will soon see that the device continues to use home country GSM network (Etisalat, UAE) until the truck crosses the border. Once the truck reaches the new territory it would automatically switch over to a new GSM provider, in this example (OmanTel, Oman).
The switch-over is achieved with a simple trick, GSM Operator code profile switching. This option allows you to define different module behaviour while the truck is in Home network and/or Roaming network.
The feature is commonly used for GPS device that is installed in cross border trucks on roaming, and the purpose is to have the device pass the location updates to the server while in Home/Roaming operator network based on a set of rules so that you can cut down on GSM data charges.
Please make sure your GPS device is updated with latest firmware and is configured with basic parameters. You may refer to Ruptela ECO4+ configuration guide for detailed configuration steps.
Step 1. Find out GSM Operator Codes
Find out GSM Operator Codes for both Home & Roaming networks
As a first step, you need to find out the GSM mobile country code from wikipedia; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_country_code. “The mobile country code consists of 3 decimal digits and the mobile network code consists of 2 or 3 decimal digits and the first digit of the mobile country code identifies the geographic region”.
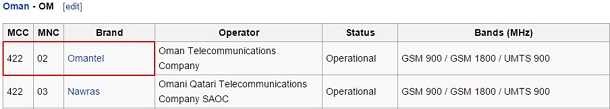
Example: Etisalat, UAE – Home operator Operator code – 4240
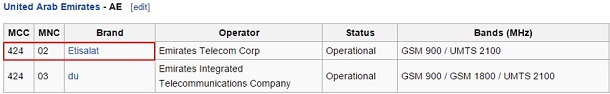
Omantel, Oman – Roaming operator Operator code – 42202
Step 2: Configure the parameters
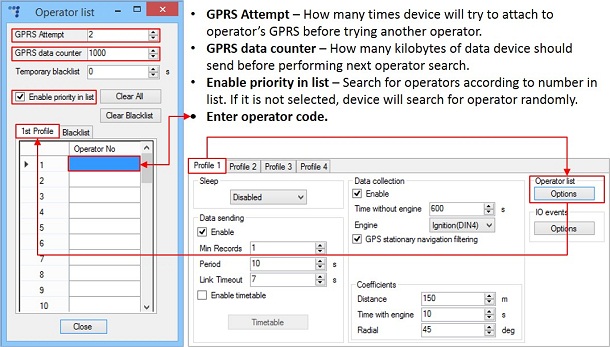
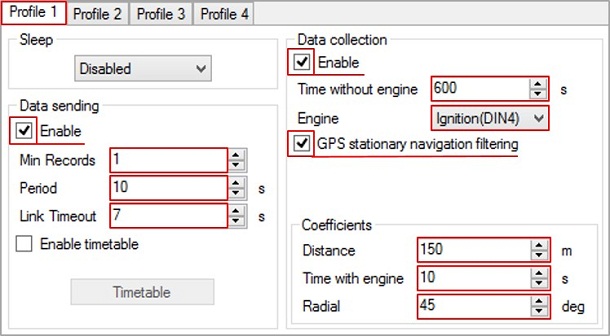
Usually Profile 1 is configured for home network. Data Coefficients and send intervals are set up depending on our requirements.
To make effective use of the profiles, it is wise to set more optimized parameters in roaming profile (Profile 2) – this usually includes larger coordinate recording intervals, packets with greater number of coordinates sending, and in some cases GPRS context available only for a certain time interval. Profile 3 may either contain operator code (rarely used) or could be empty list.
For example, under normal conditions, the GPS device uses the home network to send location updates but as soon as the truck crosses the UAE border, device detects the operator with code 42202 (Roaming operator code).
Immediately the device checks profile 1 operator list and try to match the new operator code with the entry. On mismatch it checks profile 2 operator list. The device switches to profile 2 immediately on finding a successful match.
Operator list allow selection of operators used in current profile. If operator that is in list is not found device will search for other operator in list. If no operators were found, device will switch to next profile.
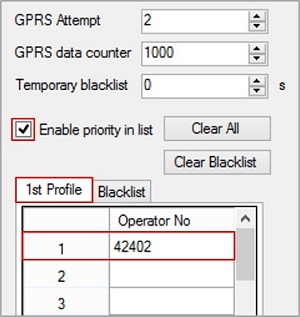

Profile is now configured for Home network.
To utilize location updates on your vehicles to max, data coefficients and data sending intervals can be set keeping a minimum gap/interval.
In this example, a location update will be sent using Home operator network in every 10 seconds or 150 meters.
Step 4. Update roaming operator profile
Omantel – Roaming operator Operator code – 42202 Add roaming operator code 42202 to 1st profile.
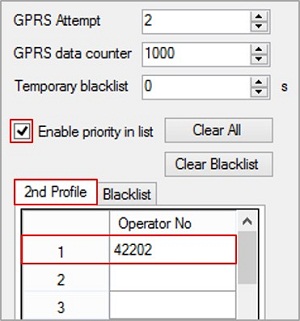
Profile 2 is now configured for Roaming network.
Step 5. Configuring data packet size
Next step is to configure data packet size & location update frequency
You know well that the data charges in roaming networks are always on a rocketing-high. To tackle this issue, it’s always advisable to keep the data coefficients & data sending frequency with a larger interval than that of home network.
- Min. records
- Period frequency
- Time frequency with engine switched off
- Distance set for data frequency
- Time with engine switched on
- Radial turn (degrees) updates.
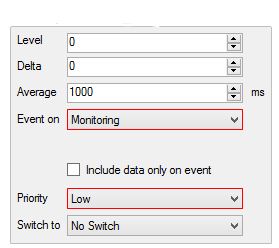
Note: It’s advisable not to set ‘High Priority’ for any IO events while roaming to reduce data packets being sent so frequently resulting in high roaming charges; however you can set that if there’s a necessity of a particular event notification to be triggered, so you could act quickly to avoid further losses on your assets.
Recommended action: Set ‘Priority’ as ‘Low’ for ‘Event on – Monitoring’.
